Malaria Facts April 2019
- April 25, 2019
- Posted by: Informed Healthcare Solutions
- Category: Client Wellness Newsletters
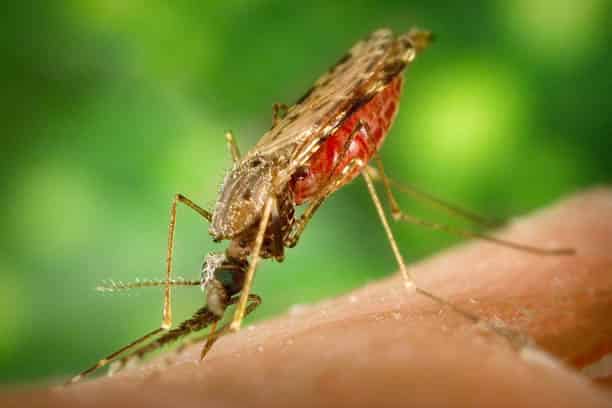
MALARIA
Malaria is a mosquito-borne disease transmitted exclusively through the bite of the female Anopheles mosquito.
Malaria infections increase in the South African summer months from September to the end of May.
The high risk areas in South Africa include:
- Far north Kwa-Zulu Natal bordering Mozambique.
- Low veld areas of Mpumalanga Province including the Kruger National Park but excluding Nelspruit and White River.
- North-eastern parts of Limpopo province.
6 key facts about Malaria:
- Malaria is preventable and curable.
- Early diagnosis and treatment reduces disease and prevents death. It also contributes to reducing malaria transmission.
- Malaria is not contagious.
- Climate conditions influence transmission as it may affect the number and survival of mosquitos such as rain patterns, temperature and humidity.
- Your own immunity is an important factor, particularly if you live in an area of moderate or intense transmission conditions.
- Transmission is more intense in places where the mosquito lifespan is longer, and where the female bites several times in one night.
Prevention:
Prevention of malaria involves protecting yourself against mosquito bites and taking anti- malarial medication.
Public health officials strongly recommend that pregnant woman and young children avoid travelling to areas where malaria is common.
If you are travelling to a malaria area you should see your health provider 4-6 weeks before travel. The health provider will take your travel plans, age, medical history, drug allergies and pregnant status into account.
How to reduce your exposure to mosquito bites apart from taking medication:
- Avoid being out from dusk to dawn.
- Wear long sleeves and trousers when outside. Use mosquito repellents.
- Stay in a room that has air conditioning, window screens and mosquito nets around the bed. Use insect repellent indoors.
Symptoms of malaria:
- Fever, chills, sweating, headaches and body aches.
- Tiredness, coughing, jaundice, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea. Confusion, hallucinations, seizures, dark or bloody urine.
Disclaimer: The information and opinions in this document have been recorded and arrived at in good faith and from sources believed to be reliable, but no representation or warranty, expressed or implied, is made to their accuracy, completeness or correctness. The information is provided for information purposes only and should not be construed as the rendering of advice. Informed Healthcare Solutions accordingly accepts no liability whatsoever for any direct, indirect or consequential loss arising from the use of this document or its contents. IHS is a licensed financial service provider: FSP # 12239
Malaria Facts April 2019